Apacheのアクセスログやエラーログを解析するとき、基本的にはawkやgrepを組み合わせて整形する事が多いだろう。
今回は、そんなApacheのログファイルをSQLで解析することが出来るツール『asql』を紹介する。
1.インストール
まずはインストールから。
Debian/Ubuntu系の場合はapt-getで、RHEL系の場合はソースからコンパイルしてインストールする。
Debian/Ubuntu系の場合
sudo apt-get install asqlRHEL系の場合
sudo yum install perl-DBD-SQLite perl-Term-ReadLine-Gnu
wget http://www.steve.org.uk/Software/asql/asql-1.7.tar.gz
tar xvfvz asql-1.7.tar.gz
cd asql
make install2.ログファイルを読み込む
さて、それでは実際にasqlを使ってログの分析を行ってみよう。
まず、asqlコマンドを実行してasqlのコンソールに入る。
asql
次に、このasqlコンソール上で以下のようにコマンドを実行し、apacheのログファイルを読み込む。
load apacheログファイルのPATH(ワイルドカード指定可能)Debian/Ubuntu系の場合
load /var/log/apache2/access.*RHEL系の場合
load /var/log/httpd/access_log*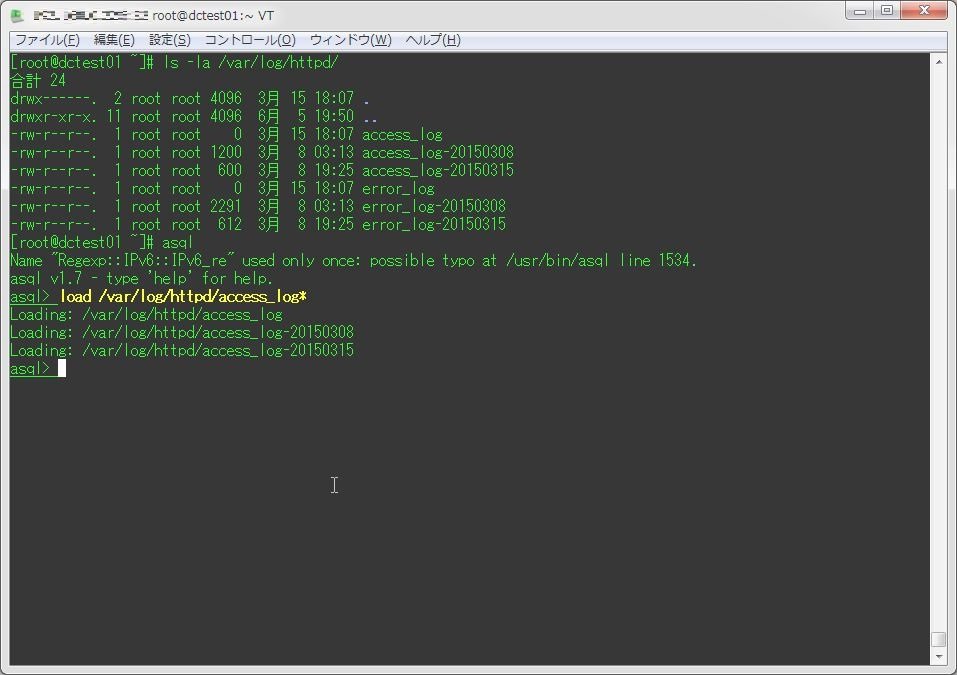
これで、SQLでapacheのログを抽出することができるようになった。
3.ログの抽出
それでは、実際にログを抽出してみよう。
なお、SQLで抽出するにあたり、SELECT文で抽出する列は以下のようになっている。
asql> show
The 'logs' table has the following columns:
id - ID of the request
source - IP, or hostname, which made the request.
request - The HTTP request
status - The HTTP status-code returned
size - The size of the response served, in bytes.
method - The HTTP method invoked (GET, PUT, POST etc).
referer - The HTTP referer (sic).
agent - The User-Agent which made the request.
version - The HTTP version used by this client.
date - The date and time at which the request was made.
label - Any label applied when the logfile was read.
user - The remote (authenticated) user, if any.それでは、試しにSELECT文を実行してみよう。
SELECT source,SUM(size) AS Number FROM logs GROUP BY source ORDER BY Number DESC;
SELECT * FROM logs ;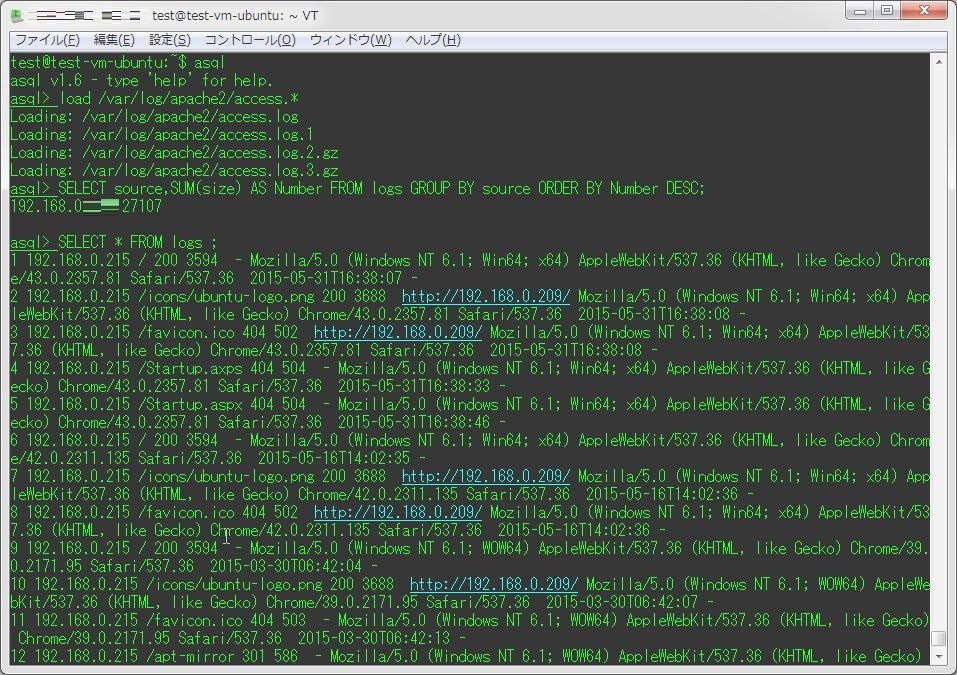
確かに、SQLでapacheのログファイルから抽出を行う事が出来た。
なお、ログからデータベースに取り込んだファイルを保存する場合は、asqlコンソール内でsaveコマンドを、読み込む場合にはrestoreコマンドを利用する。

