LinuxやUNIXでbashを利用しているならば、historyコマンドにお世話になっている人も多いだろう。
そんなhistoryコマンド、デフォルトでは基本的にコマンドの実行時間は記録されない。
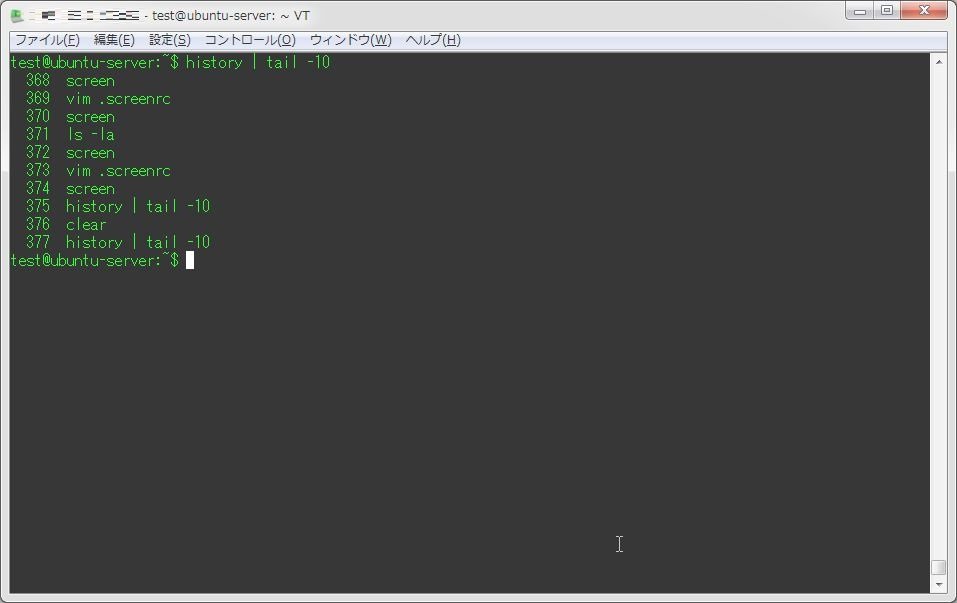
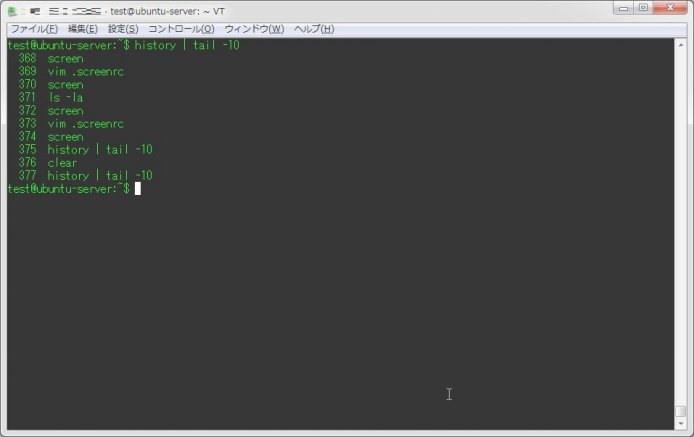
test@ubuntu-server:~$ history | tail -10
368 screen
369 vim .screenrc
370 screen
371 ls -la
372 screen
373 vim .screenrc
374 screen
375 history | tail -10
376 clear
377 history | tail -10
test@ubuntu-server:~$
そんなhistoryコマンドの実行結果でタイムスタンプを出力させる場合は、「.bash_rc」に以下の一行を追記する。
これで、追記以後のログインからコマンドの実行時間を記録するようになる。
export HISTTIMEFORMAT='%F %T '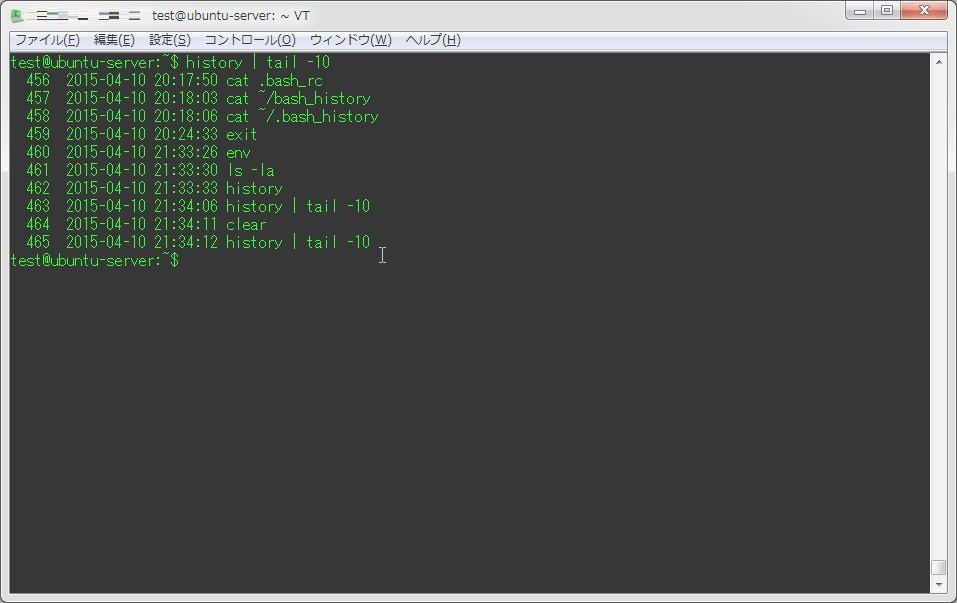
test@ubuntu-server:~$ history | tail -10
456 2015-04-10 20:17:50 cat .bash_rc
457 2015-04-10 20:18:03 cat ~/bash_history
458 2015-04-10 20:18:06 cat ~/.bash_history
459 2015-04-10 20:24:33 exit
460 2015-04-10 21:33:26 env
461 2015-04-10 21:33:30 ls -la
462 2015-04-10 21:33:33 history
463 2015-04-10 21:34:06 history | tail -10
464 2015-04-10 21:34:11 clear
465 2015-04-10 21:34:12 history | tail -10なお、同一ユーザーで複数のウィンドウを開いている場合、historyの内容が共有されず残らない。
このため、以下の内容を.bashrcに記述しておくといいだろう。
export HISTCONTROL=ignoredups:erasedups # historyに重複したコマンドを記録しない
export HISTSIZE=100000 # 現在のセッションで利用しているhistoryの履歴数を定義する
export HISTFILESIZE=100000 # 「.bash_history」で記録する履歴数を定義する
shopt -s histappend # 「.bash_history」への記録方式を追記にする
export PROMPT_COMMAND="history -a; history -c; history -r; $PROMPT_COMMAND"これで、同一ユーザに複数ウィンドウで同時にログインしていた場合でもログが残るようになった。

